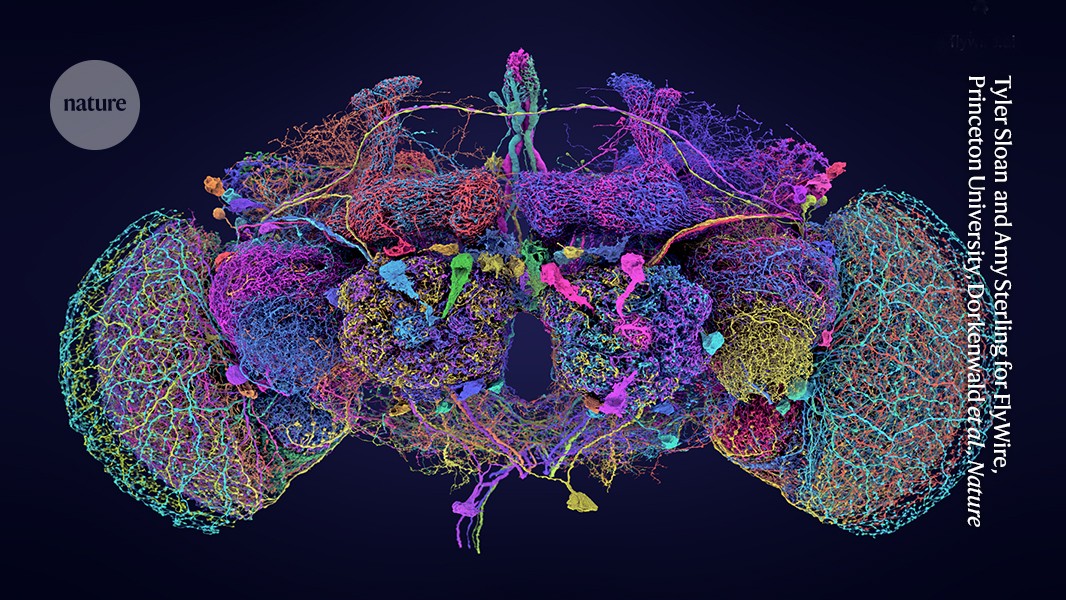
"… Researchers are hoping to do that now that they have a new map — the most complete for any organism so far — of the brain of a single fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). The wiring diagram, or ‘connectome’, includes nearly 140,000 neurons and captures more than 54.5 million synapses, which are the connections between nerve cells.
… The map is described in a package of nine papers about the data published in Nature today. Its creators are part of a consortium known as FlyWire, co-led by neuroscientists Mala Murthy and Sebastian Seung at Princeton University in New Jersey."
See the associated Nature collection: The FlyWire connectome: neuronal wiring diagram of a complete fly brain, which also has links to the nine papers
All nine papers are open access!


In a physical (as in physics) sense, it’s because software neural nets are inherently digital, whereas actual neurons function in the analog (in terms of electrical impulses, as well as chemically) domain. We don’t have tech to accurately and effectively represent all of that.
Audio is inherently analogue, but you can record it into digital formats just fine.
It’s tempting to say “well, that’s different though” but it really isn’t.
Just like with audio, you’ll need high enough fidelity encoding to make it all work, otherwise you end up with garbage.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organ-on-a-chip