

Are there still people out there moaning that “Americans won’t vote for a woman,” despite, y’know, Hillary Clinton winning the popular vote in 2016?


Are there still people out there moaning that “Americans won’t vote for a woman,” despite, y’know, Hillary Clinton winning the popular vote in 2016?


Interesting that it’s turning out so similarly, then.


No, they just believe that they are God’s chosen people. Totally different.


I make my guess that there are two factors:
The Baader-Meinhof Phenomenon (or frequency illusion If somebody has a chip on their shoulder about rude Linux users, the rude Linux users they see will be highly memorable.
People tend to get back the same energy that they project to other people.
My instance has a very laissez-faire policy, so it’s federated with almost everybody. My experience is the same; I’ve only ever seen self-aware mocking of the Linux-user attitude.


Hey, wasn’t this supposed to be an actual dome? The demented, old dingbat described it as a literal dome.


So, essentially the same as a company spokesperson!


Forget the spokesperson, just ask Google AI directly:
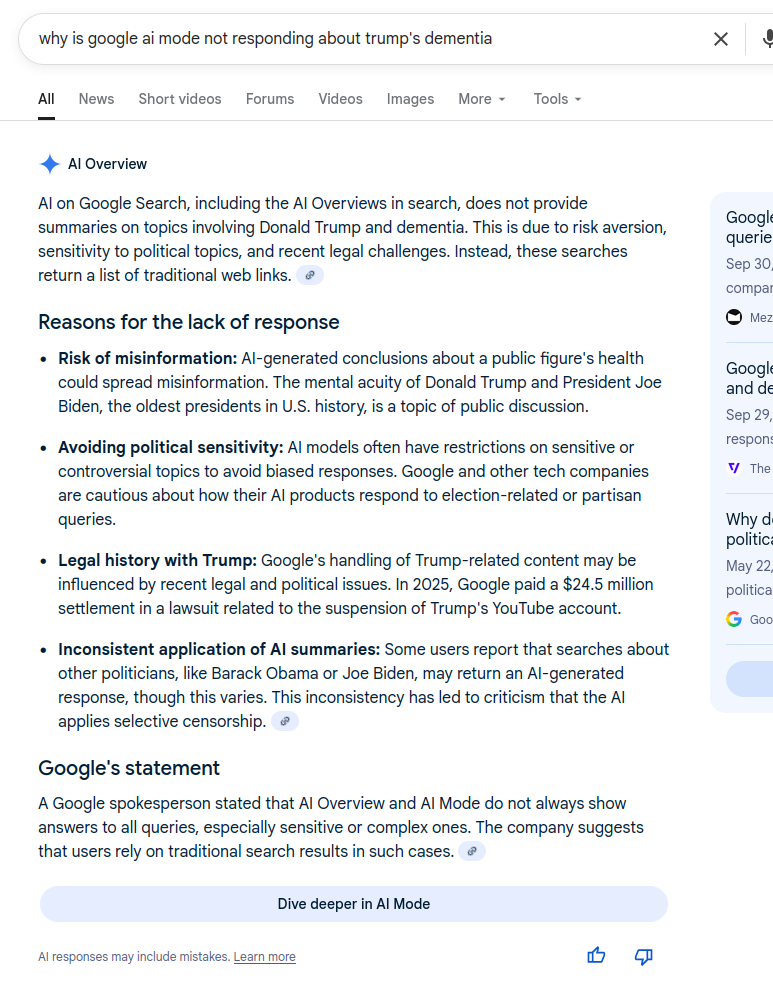
AI on Google Search, including the AI Overviews in search, does not provide summaries on topics involving Donald Trump and dementia. This is due to risk aversion, sensitivity to political topics, and recent legal challenges. Instead, these searches return a list of traditional web links.
Reasons for the lack of response
- Risk of misinformation: AI-generated conclusions about a public figure’s health could spread misinformation. The mental acuity of Donald Trump and President Joe Biden, the oldest presidents in U.S. history, is a topic of public discussion.
- Avoiding political sensitivity: AI models often have restrictions on sensitive or controversial topics to avoid biased responses. Google and other tech companies are cautious about how their AI products respond to election-related or partisan queries.
- Legal history with Trump: Google’s handling of Trump-related content may be influenced by recent legal and political issues. In 2025, Google paid a $24.5 million settlement in a lawsuit related to the suspension of Trump’s YouTube account.
- Inconsistent application of AI summaries: Some users report that searches about other politicians, like Barack Obama or Joe Biden, may return an AI-generated response, though this varies. This inconsistency has led to criticism that the AI applies selective censorship.
Google’s statement A Google spokesperson stated that AI Overview and AI Mode do not always show answers to all queries, especially sensitive or complex ones. The company suggests that users rely on traditional search results in such cases.


Armenia and Cambodia are screwed.


Here’s the crux of the difference of opinion: No, Pres. Harris would not have been talking about luxury hotels on the rubble of Gaza. Israel, however, has been talking about it for years. The U.S. President has very little influence over Israeli intentions, and whether the U.S. President talks about it sounds like an objection based on style rather than substance.


I get the thinking here, but past bubbles (dot com, housing) were also based on things that have real value, and the bubble still popped. A bubble, definitionally, is when something is priced far above its value, and the “pop” is when prices quickly fall. It’s the fall that hurts; the asset/technology doesn’t lose its underlying value.


You are correct. I forgot to qualify my statement to say that it applies on city streets. Apologies, I can’t find the YouTube video that discussed the study right now.


Hi-viz doesn’t do anything. There’s no statistical difference in casualty rates between people wearing it and people not. Consider that drivers routinely plow into the back of emergency vehicles stopped by the side of the highway, completely wrapped in hi-viz, reflective material, and with million-lumen flashing lights. This is victim-blaming nonsense.


How DARE people move around the landscape in the traditional way that humans have been locomoting for tens of thousands of years without considering YOUR needs!
(That is, if you can’t see what’s in front of your car, you need to slow down.)
e: typo


Best President since Jimmy Carter is a low, low bar. We forget that Carter was a neo-liberal who threw labor under the bus. Because the Presidents since have been so right-wing, he looks like a leftist in the rear view. And throwing the working classes under the bus is one of the major reasons we’re here now.


Can we start delivering those 2,000lb. bombs that the U.S. gives to Israel one by one, to Netanyahu’s house, by airmail?


Fascinating how the subtext is always that we should feel comforted because a mass-casualty event that’s a normal part of the system that kills and injuries people every day isn’t terrorism.
“Oh, that’s just the machine crushing orphans. It’s supposed to be doing that.”


There are multiple meanings of “support.” There’s an endorsement meaning, which can be explicit or tacit, and there’s an aiding meaning. The Democrats may not explicitly endorse it, but the Biden administration certainly did tacitly endorse it by directly aiding it. And most of the party has been tacitly endorsing and aiding it for decades.


Huh, that’s really odd conclusion to draw from Democrats literally supporting genocide. Harris couldn’t even be bothered to come out against it during the campaign even when they knew their support was a losing issue.


It’s a simple moral calculus, don’t you see? You must always vote for Hitler and help him kill 5,000,000 people, if the alternative is somebody who’s going to kill 5,000,001 people.
Linux requires tinkering and Windows doesn’t? Is that some alternate-universe version of Windows? In my experience, the difference is social/psychological. When Windows fucks up, “everybody uses it,” so the blame falls on the masses, not the user, who was just going along with what’s normal and expected. People sort of mentally elide memory of the Windows fuck ups, because that’s just how Windows is.
Linux is different and weird, and you have to stray from the herd to use it. Straying from the masses is scary, because when Linux fucks up, it’s your fault for being contrary. That threat to one’s place in the social order is quite memorable. Hence the reluctance of Windows users, who hate it, to even consider trying another OS that they know nothing about.
I never switched from Windows. I never used Windows as my main OS. I had an Amiga, then learned Unix on SunOS, so I was used to being weird. Once I got a PC, I used FreeBSD. It did require a lot of fiddling back in those days, and when I got tired of that, I switched to Ubuntu, which was amazing in that it Just Worked™. (Aside from manual installation of the Windows driver for the PCMCIA WiFi card with NDISWrapper.)
(I still do tinker with it, and sometimes break it, but the base OS has been rock solid. I noticed the other day that my main PC was installed with Ubuntu 18.04, and upgraded to 24.04.)